The management of erectile dysfunction (ED) has evolved significantly since the late 1990s, when the introduction of sildenafil citrate redefined both pharmacology and male sexual health. Yet, despite its clinical success, oral sildenafil still faces the same pharmacokinetic barriers that have challenged physicians and patients for decades: delayed onset, variable bioavailability, and gastrointestinal side effects. For many men, these drawbacks undermine spontaneity, satisfaction, and treatment adherence.
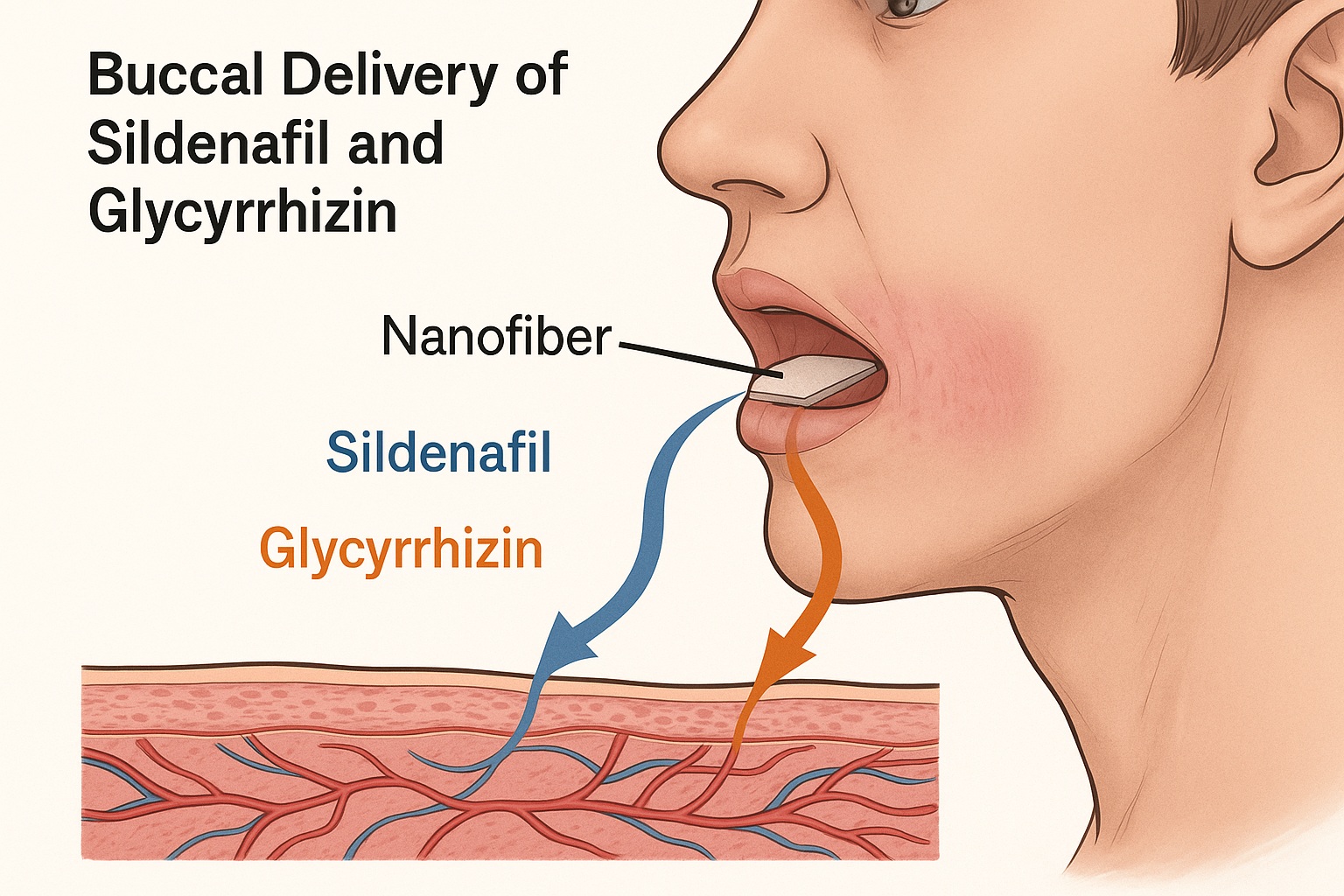
Recent advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery are reshaping this landscape. Among them, the buccal nanofiber delivery system—a thin, rapidly dissolving film applied to the inner cheek—has emerged as a practical and elegant solution. A new study proposes an even more sophisticated approach: electrospun nanofibers loaded with sildenafil and glycyrrhizin, designed for fast, safe, and efficient absorption directly through the oral mucosa.
This innovation represents more than a new dosage form. It signifies a shift in therapeutic strategy—from systemic dosing toward localized, patient-friendly, and rapid-onset delivery, with the potential to transform how clinicians approach ED management.
The Persistent Challenges of Conventional Sildenafil Therapy
Oral sildenafil, while effective, presents several clinical limitations that often frustrate both patients and physicians. After ingestion, the drug undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism, reducing its bioavailability to roughly 40%. Peak plasma concentrations occur 30–120 minutes post-dose, leading to a delay in onset that may hinder spontaneity in sexual activity.
Additionally, systemic exposure can trigger adverse effects such as headache, flushing, nasal congestion, and dyspepsia—symptoms that, while mild, contribute to non-adherence in up to 30% of users. These pharmacologic and behavioral barriers have prompted the search for alternative routes of administration capable of delivering sildenafil more efficiently and with fewer systemic effects.
The buccal mucosa offers a compelling alternative. Its high vascularization and permeability, coupled with a bypass of hepatic first-pass metabolism, make it an ideal site for rapid systemic drug absorption. Unlike sublingual or transdermal formulations, buccal delivery can sustain intimate contact between drug and tissue without discomfort or interference with speech and swallowing.
From a clinical standpoint, a buccal system that achieves faster onset, lower dosing, and higher patient comfort could represent a major step forward in ED therapy—bridging the gap between pharmacologic efficacy and real-world usability.
Nanofiber Technology: Redefining Drug Delivery Through the Oral Mucosa
Nanofiber systems are ultra-thin matrices composed of polymeric filaments less than one micrometer in diameter. Produced via electrospinning, these fibers create an interconnected network capable of encapsulating and protecting drug molecules while enabling precise control over dissolution and release kinetics.
In the study under discussion, researchers employed polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)—a hydrophilic, biocompatible polymer known for its rapid solubility and stability—as the structural base. By integrating sildenafil citrate and glycyrrhizin (a natural bioavailability enhancer derived from licorice root), they created a dual-loaded nanofiber that dissolves within seconds upon contact with saliva, releasing the active ingredients directly into the buccal circulation.
The electrospun fibers were characterized by:
- Uniform morphology with smooth, bead-free surfaces under scanning electron microscopy (SEM);
- Average fiber diameters below 500 nm, ensuring high surface area and immediate disintegration;
- Excellent drug encapsulation efficiency, with both sildenafil and glycyrrhizin uniformly distributed within the polymeric matrix.
From a formulation science perspective, this is a sophisticated yet clinically practical design. The fibers are flexible, transparent, and easy to apply, requiring no special equipment for administration—making them particularly suitable for home use or discreet application before sexual activity.
The Role of Glycyrrhizin: More Than a Sweetener
The inclusion of glycyrrhizin (GLY) in the nanofiber formulation is not merely for taste. Clinically, this compound offers a dual advantage that enhances both patient acceptability and pharmacologic performance.
First, glycyrrhizin serves as a natural sweetener and mucoadhesive agent, improving the comfort and retention of the buccal patch. Second, and more importantly, it functions as a bioavailability enhancer by modifying membrane permeability and inhibiting efflux transporters such as P-glycoprotein. This facilitates greater mucosal absorption of sildenafil—an advantage particularly relevant given sildenafil’s moderate lipophilicity and limited passive diffusion through biological membranes.
Moreover, glycyrrhizin possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which may reduce local irritation and oxidative stress at the mucosal interface. In preclinical testing, cell viability remained above 80%, confirming that the dual-drug nanofiber is both safe and well tolerated by epithelial tissues.
The synergy between sildenafil and glycyrrhizin thus extends beyond chemistry—it represents a harmonization of efficacy, safety, and patient experience.
Performance Evaluation: Fast, Effective, and Clinically Relevant
The buccal nanofibers demonstrated remarkable disintegration and release properties, tailored for clinical relevance. Upon application, the fibers disintegrated within four seconds, releasing sildenafil and glycyrrhizin rapidly into the buccal environment. Complete drug release was achieved within 120 minutes, ensuring a sustained yet swift absorption phase—ideal for achieving prompt onset without abrupt peaks in plasma concentration.
In vitro and ex vivo assessments confirmed high drug permeability through porcine buccal mucosa, a well-established analog for human tissue. The nanofibers maintained structural integrity until dissolution, ensuring predictable release kinetics.
The drug release profile followed a diffusion-controlled mechanism, balancing rapid onset with prolonged therapeutic presence. This pharmacokinetic behavior is especially relevant for ED management, where consistent plasma levels can enhance sexual confidence and spontaneity—two key determinants of patient satisfaction.
From a clinical performance perspective, the formulation checks all major boxes:
- Fast-acting for improved spontaneity,
- Non-invasive and user-friendly,
- Predictable pharmacokinetics with reduced systemic side effects,
- Enhanced patient adherence through comfort and discretion.
Such a profile makes the buccal nanofiber system particularly attractive for patients dissatisfied with conventional oral tablets or those experiencing gastrointestinal intolerance.
Translating the Technology: Clinical Opportunities and Patient Benefits
For physicians managing erectile dysfunction, the buccal nanofiber system represents an evolutionary step in drug delivery—not a replacement, but an enhancement of existing pharmacotherapy. The clinical implications are significant across several domains:
- Improved onset of action: The direct mucosal absorption bypasses the hepatic first-pass effect, potentially reducing time to onset from 45–60 minutes (oral route) to less than 15 minutes.
- Lower required dose: Enhanced bioavailability means smaller doses can achieve equivalent efficacy, minimizing the risk of adverse effects.
- Greater patient compliance: The convenience of a discreet, tasteless, fast-dissolving film aligns with modern patients’ demand for comfort and control.
For specific populations—such as elderly men, those with hepatic impairment, or patients on polypharmacy regimens—the buccal route could reduce drug-drug interactions and improve overall safety.
Moreover, this delivery system may bridge an important psychosocial gap. Erectile dysfunction is not merely a vascular condition; it is often psychologically charged, and any delay or unpredictability in drug effect can undermine confidence and performance. A formulation that acts quickly and reliably could therefore have an outsized impact on quality of life and sexual relationships.
Comparing Buccal Nanofibers to Other Novel Delivery Systems
The pharmaceutical industry has explored numerous strategies to overcome sildenafil’s bioavailability challenges—ranging from orodispersible tablets and sublingual films to intranasal sprays and transdermal patches. Each offers certain advantages, yet few have achieved the optimal balance between onset speed, safety, and convenience.
Buccal nanofibers, however, present several distinguishing features:
- Superior mucoadhesion: The electrospun structure ensures intimate contact with mucosal tissue, promoting sustained absorption.
- Minimal residue: The film dissolves completely, avoiding the aftertaste or residue often reported with sublingual systems.
- Thermal stability: Nanofibers remain stable under normal storage conditions, preserving sildenafil’s integrity.
- Combination potential: Multiple agents—such as nitric oxide donors or natural vasodilators—could be co-encapsulated for enhanced efficacy.
In essence, the nanofiber platform combines the immediacy of sublingual formulations with the precision and control of transdermal systems, making it uniquely suited for the needs of ED patients.
Safety and Biocompatibility: A Prerequisite for Clinical Adoption
Safety remains paramount in any translational innovation. The researchers conducted comprehensive biocompatibility testing using oral epithelial cell cultures to evaluate cytotoxicity and structural compatibility. Results demonstrated >80% cell viability across all formulations, confirming excellent tolerability.
The absence of inflammatory markers or morphological alterations under microscopy supports the system’s suitability for repeated or long-term use. Unlike certain mucoadhesive polymers that can irritate mucosal tissues, PVP and glycyrrhizin maintain a neutral pH and gentle biointerface.
In addition, the nanofibers’ mechanical flexibility prevents microabrasions or discomfort during application—an important consideration for patient adherence. From a regulatory perspective, both core components (PVP and sildenafil) are already FDA-approved for other routes, simplifying future clinical translation and approval pathways.
Beyond Erectile Dysfunction: Broader Therapeutic Implications
Although designed for ED, the buccal nanofiber delivery platform holds broader potential. Its versatility allows encapsulation of drugs that require rapid systemic absorption or are degraded by gastrointestinal metabolism.
Potential applications include:
- Cardiovascular agents, such as nitrates or beta-blockers for acute hypertension management;
- Pain control, using opioids or NSAIDs for breakthrough episodes;
- Hormonal therapies, such as testosterone or peptide-based agents requiring stable systemic levels.
For the sexual medicine field, this technology could also support combination therapies—for example, co-delivery of sildenafil with antioxidants or endothelial-protective agents to address underlying vascular dysfunctions.
In this sense, the buccal nanofiber platform is not merely a reformulation; it is a scalable clinical technology with implications across multiple therapeutic domains.
Challenges and the Path Toward Clinical Implementation
While the promise of buccal sildenafil nanofibers is compelling, several translational hurdles remain.
- Manufacturing scalability: Electrospinning must be adapted for large-scale, reproducible production under Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards.
- Dosage standardization: Uniform drug loading and film thickness are essential to ensure consistent dosing.
- Clinical validation: Human pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies must confirm efficacy, safety, and patient satisfaction compared to oral tablets.
Furthermore, patient education will be vital. Although simple to use, buccal patches represent a new paradigm; clinicians will need to counsel patients on correct application, timing, and potential interactions (e.g., with food or oral hygiene products).
Nonetheless, these challenges are surmountable—and given the unmet need for more flexible, patient-centered ED therapies, clinical trials are both feasible and timely.
Conclusion: Toward Smarter, Patient-Centered Therapy in Erectile Dysfunction
The development of sildenafil/glycyrrhizin-loaded buccal nanofibers is a striking example of how material science can translate into meaningful clinical innovation. By merging nanotechnology, pharmacology, and patient-centric design, this approach offers a practical solution to long-standing challenges in ED therapy: delayed onset, variable absorption, and inconsistent patient adherence.
For clinicians, this technology signals the next phase in sexual medicine—where precision in pharmacokinetics meets simplicity in application. For patients, it offers what they have long desired: a fast, effective, and discreet therapy that restores not only function but also confidence.
As translational research advances, the buccal nanofiber system could soon redefine how we deliver not just sildenafil, but a new generation of fast-acting therapeutics—proving once again that innovation in medicine often begins with understanding the patient’s lived experience as much as their physiology.
FAQ: Buccal Sildenafil Nanofiber Therapy
1. How fast can buccal sildenafil nanofibers take effect compared to oral tablets?
Because the drug is absorbed directly through the oral mucosa, onset could occur within 10–15 minutes, much faster than the 45–60 minutes typical for oral sildenafil.
2. Are there any expected side effects unique to the buccal system?
No major new side effects are expected. The system reduces systemic exposure, so common adverse effects like flushing or headache may actually be less frequent.
3. When might this technology reach clinical use?
If early human trials confirm safety and efficacy, the formulation could advance toward commercialization within 3–5 years, particularly given that its core components are already clinically approved.